Phenoxy Resins (Polyhydroxyl Ethers)
Properties
Phenoxy resins are amorphous thermoplastic polymers and thermosetting resins. These polymers have terminal hydroxyl groups as well as hydroxyl groups in every repeat unit and thus can be classified as polyhydroxyethers. They are derived from bisphenol A [(CH3)2C(C6H4OH)2] and epichlorohydrin [Cl-CH2-(C2H3O)]. The reaction is typically carried out in a solvent such as methyl ethyl ketone or PM acetate with an excess amount of bisphenol to ensure no epoxide remains. The reaction yields linear phenoxy resins of high molecular weight (10,000 - 100,000 g/mol) and with narrow polydispersity. Their idealized structure is shown below
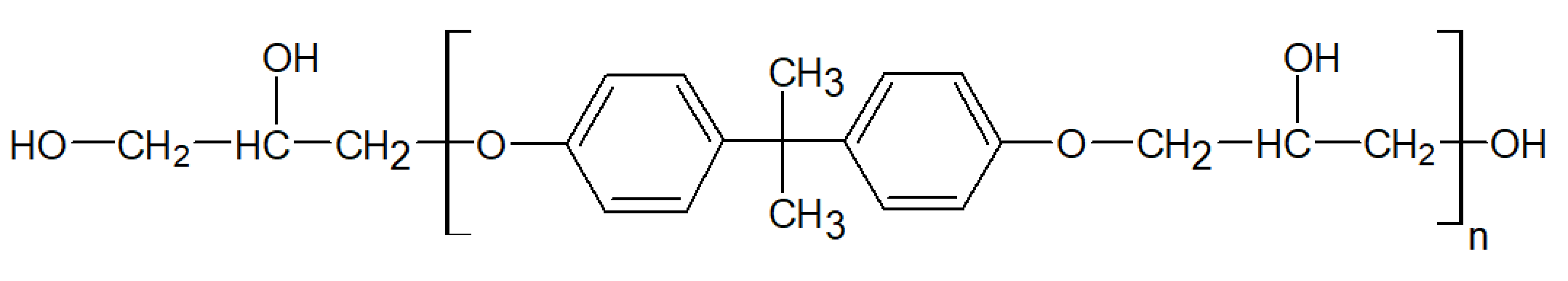
Phenoxy resins are often heat cured with isocyanates or anhydrides among other chemicals to produce thermosetting polymers. They have excellent mechanical properties including flexibility, toughness, adhesive and cohesive strength, as well as chemical and heat resistance. However, when reacted (cross-linked) with a curative, the mechanical properties also depend on the curative-phenoxy ratio. Phenoxies also have good vapor and oxygen barrier properties and are generally compliant with 21CFR175.300 for direct and indirect food and beverage contact.
As with other classes of thermoset polymers, blending with other resins, as well as use of additives, plasticizers and fillers is common to to reduce cost and to achieve the desired processing and final properties. Due to their high polarity, they are generally miscible with polar solvents and plasticizers as well as with many polar resins such as epoxies, phenolics, polyurethanes, polyesters, and nylons but are generally incompatible with polyacrylates, polyolefins, and polyvinyls.
COMMERCIAL Phenoxy Resins
Commercial grades of phenoxy resins are available in a wide variety of forms, including liquid, solid, dissolved in solvent, and dispersed in water. Major manufacturers are Gabriel, Kukdo Chemicals, Shin-A T&C, and Hexion.
APPLICATIONS
Phenoxy resins are often blended with epoxy and phenolic resins to enhance their performance properties. They are used in a wide variety of products including coatings, adhesives, inks, fiber sizings, composites, prepregs, and molded parts. Due to their excellent adhesion properties as well as outstanding corrosion and heat resistance, they are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industry.